- Home
- /
- Services
Energy Efficiency Services


Energy Efficiency Services
Global energy demand is expected to double by 2050, and increasing environmental concerns have led to more stringent energy efficiency regulations worldwide. The transition to these regulations, with the aim of reducing their impact on industrial businesses and facilitating the shift, has been phased in over a specific timeframe. While this transition initially imposes an additional cost on businesses, considering that a significant portion of industrial electricity is consumed by these motors, the long-term energy savings that can be achieved make the transition process attractive to businesses. The purchase cost of a motor corresponds to about 1/40 of the operational cost.
Efficiency is the goal of achieving maximum benefit with minimum effort. In many fields, such as industry and manufacturing, high efficiency is always expected. The general physical formula for efficiency is:
[EFFICIENCY = OUTPUT VALUE / INPUT VALUE] X100 (%EFFICIENCY)
As an example of energy efficiency in any motor, the formula can be expressed as:
[Motor Energy Efficiency = Output Energy / Input Energy].
Electric motors consist of two parts: one fixed (stator) and the other rotating on its own axis (rotor). Their purpose is to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electric motors account for 36% of electricity in buildings and 70% in the industrial and manufacturing sector today. Therefore, energy efficiency in electric motors is becoming increasingly important.
Losses in electric motors occur due to stator, rotor winding losses, and heat losses caused by friction. To achieve high efficiency, these losses need to be minimized.
Motor Efficiency Factors:
Frame Losses
Stator Resistance
Rotor Resistance
Windage and Friction
Additional Losses
Input Power: 100%
Output Power: Approximately 92.4%
Total Losses: Approximately 7.6%
How to Increase Electric Motor Efficiency?
Improving efficiency in motor systems is crucial for performance and energy savings. To enhance the efficiency of motors, certain practices are necessary, including:
Maintenance:
Regular motor maintenance is essential for the motor's performance, lifespan, and efficiency. Motor maintenance is divided into preventative and predictive categories. Motor maintenance should be performed regularly and not neglected. Proper motor maintenance can change energy consumption by up to 30%.
Motor Management Plan:
A motor management plan includes setting up a motor survey and monitoring program, creating spare parts inventory, and developing a maintenance plan. Having a good motor management plan for a facility is crucial for energy management strategy.
High-Efficiency Motor Energy Labels:
High-efficiency motors demonstrate better efficiency compared to other motors due to their design and materials. Using these motors has a significant impact on facility efficiency.
Voltage Imbalance:
Reducing voltage imbalance and harmonics aims to minimize vibration and stress in motors, preventing a drop in performance. The necessary voltage level should be provided for this purpose.
Other practices include using the right motor size, using adjustable speed drives, and power factor correction.
Efficiency Classes and Savings Potential in Electric Motors:
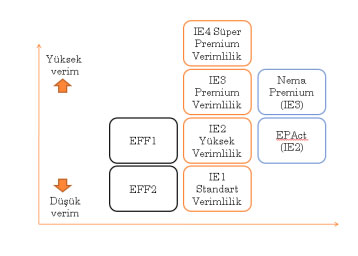
According to IEC 60034-30 standards, efficiency classes for electric motors range from 0.75 kW to 375 kW.
IE1: Standard Efficiency
IE2: High Efficiency
IE3: Premium Efficiency
IE4: Super Premium Efficiency
The transition to efficient electric motors has been the subject of numerous domestic and international projects. For example, under the commercial rebate program implemented by the United States, a certain level of financial support is provided for each horsepower, and investments in the purchase of taxable income energy-saving equipment are eligible for a 100% support in the first year. A similar program carried out in Ireland offers 100% capital support for the purchase of energy-efficient equipment. In Turkey, efforts related to electric motors include financial incentives, performance standards, and programs aimed at education and capacity development.
Join Our Newsletter
Be informed about innovations about us
